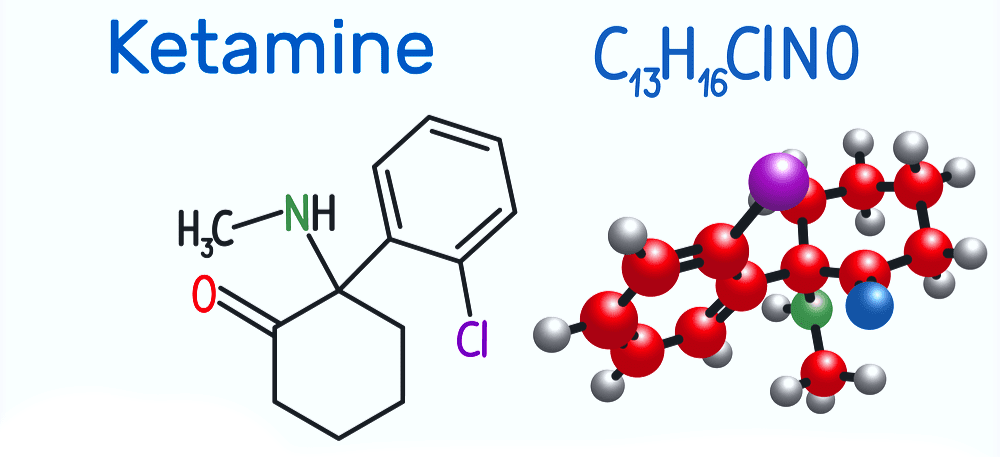
What is Ketamine? And How Does It Treat Depression?
Traditional antidepressants work by managing the brain’s chemical balance of serotonin and dopamine. Unfortunately, antidepressants like Prozac and Lexapro can trigger serious side effects and take weeks to kick in. This lag time can be critical for patients suffering from extreme anxiety or suicidal thoughts, and in need of a fast, safe solution
Thankfully, a solution exists that’s swift and effective: Ketamine. Ketamine has been approved for use in anesthesiology since the 1970s. New research proves ketamine is a viable alternative for patients suffering from treatment-resistant depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts. In fact, for many patients, small doses of ketamine, delivered via 60-minute infusions, can provide life-changing relief. The most recent ketamine studies indicate up to 83% of patients see an improvement after ketamine therapy.
“These findings take us a big step forward as we begin to fully understand the potential and limitations of ketamine’s antidepressant qualities,” says lead researcher Colleen Loo from the University of New South Wales in Australia.
So How Does It Work?
At its most basic, Ketamine works by altering the way the brain’s cells communicate. It is believed ketamine works because it influences several of the brain’s receptors associated with pain and depression, including opioid receptors and NDMA, a receptor typically associated with depression.
“If you think of it in terms of a computer, what ketamine does is a hardware fix — not like antidepressants, which are like a software fix,” says Glen Brooks, MD, an anesthesiologist and medical director of NY Ketamine Infusions.
So why does ketamine work so fast? Traditional antidepressants – aka SSRIs – work on the molecular level by essentially “switching on” G proteins. Because SSRIs must work via absorption and accumulation, it can take days for the “on switch” to be activated, and even longer before the patient feels a real difference.
In studies, researchers discovered that the administration of ketamine rapidly shuffles G proteins – sometimes in as little as 15 minutes. Even more significantly, with a ketamine treatment, the dissipation of G proteins (which can trigger depression and anxiety) is much slower than with SSRIs.
Why Choose Ketamine?
The latest studies associated with ketamine treatment for depression reveal that up to 83% of patients see an improvement after ketamine therapy. Additionally, these studies show that between 60% and 70% of patients with treatment-resistant depression respond positively to ketamine treatment.
For critical patients, it’s the swiftness of ketamine’s effectiveness that is most significant. While standard antidepressant medications can take weeks or months to take effect, ketamine works much more quickly — patients often feel relief within minutes of treatment. Additionally, ketamine’s therapeutic effect lingers – up to a week or more, even after the chemical itself is no longer in the body.
“We show that infusion of ketamine into just one brain region is sufficient to cause rapid antidepressant effects,” says neuroscientist Hailan Hu of Zhejiang University in China, leader of the team that conducted two ketamine studies. “It’s like a machine-gun shooting versus single shooting, so it carries information more efficiently to downstream brain areas,”
While it’s been difficult to conduct large-scale studies of ketamine, the consistent results of smaller clinical trials have convinced doctors around the country, who are excited by the results.
“In the past 20 years, I’ve not seen anything like this,” says Dr. Cristina Cusin, a clinician and researcher who runs the ketamine clinic at Massachusetts General Hospital.
“I still think it’s the most exciting treatment to come in mood disorders, probably of the last 50 years,” agrees Sanacora.